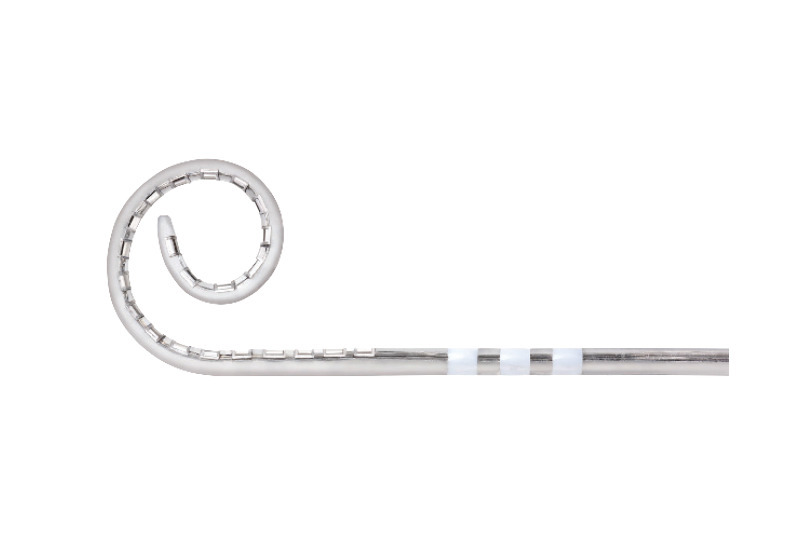
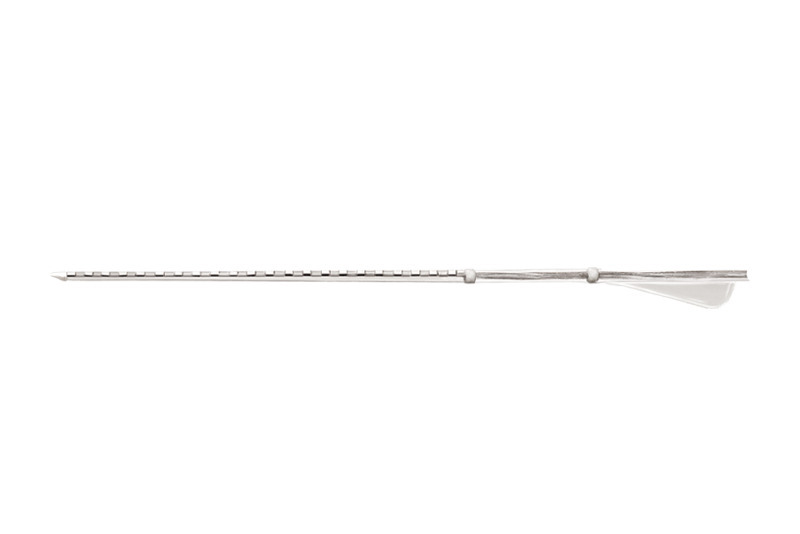
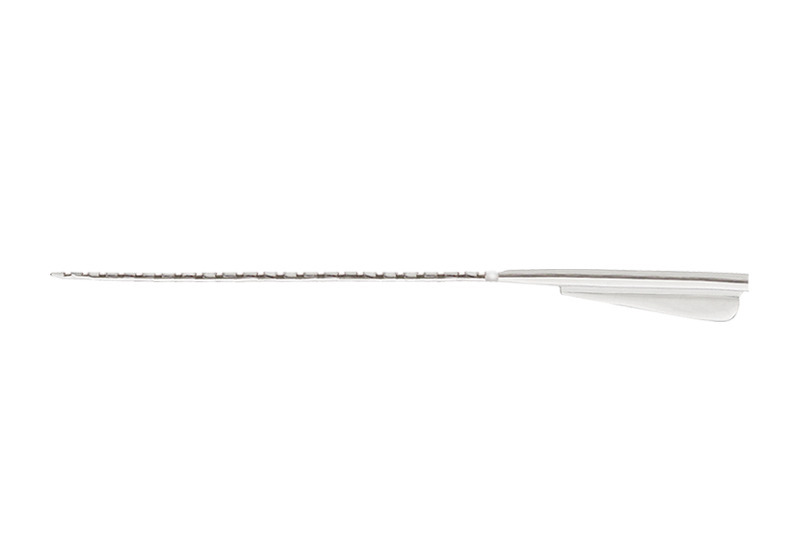
Contour Advance® Electrode (CI612)
Industry’s longest-standing perimodiolar electrode with a design that allows for focused stimulation of the cochlea.
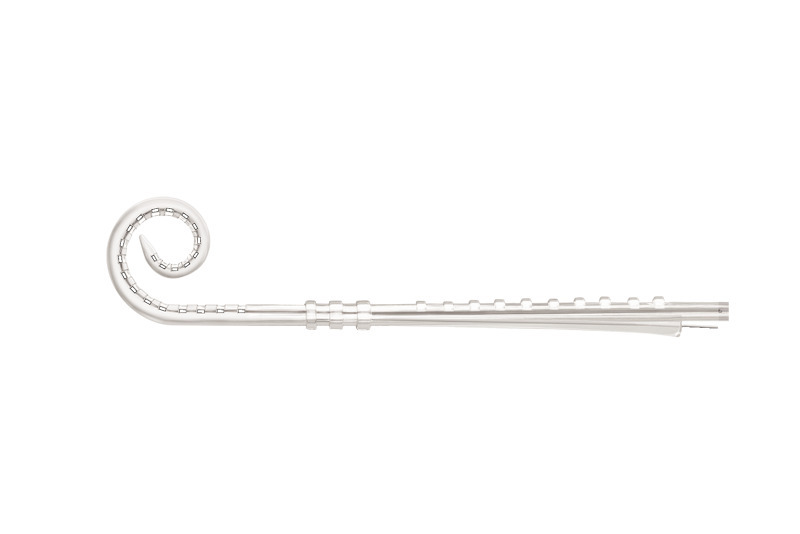

Contour Advance Electrode (CI612)
- The Contour Advance Electrode is indicated for extended round window and cochleostomy surgical approach.
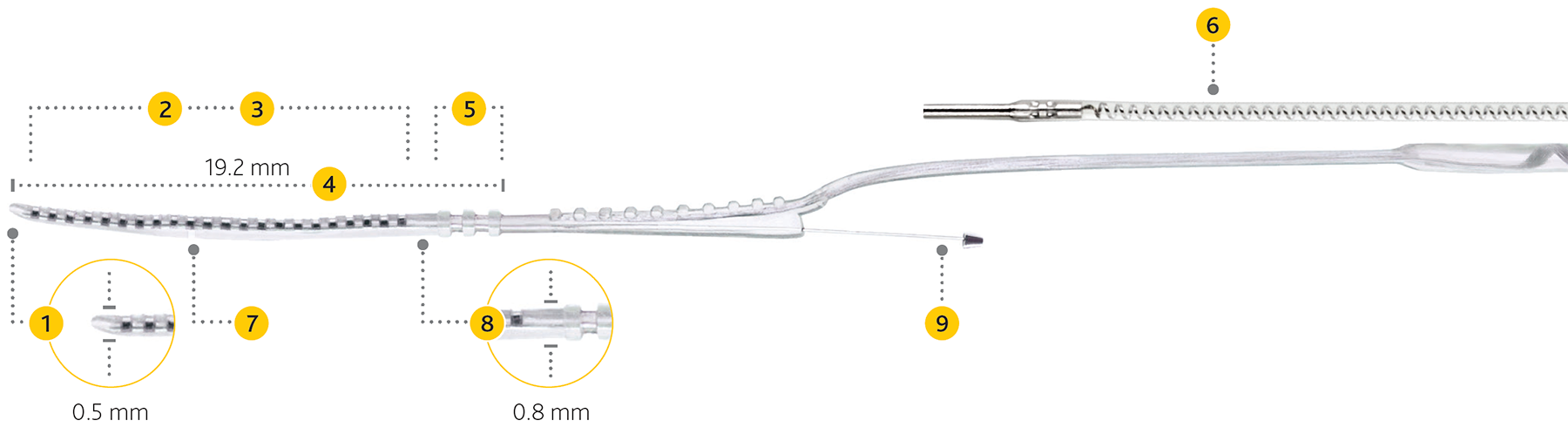
- Softip™ measuring 0.3mm diameter at apical end, proven to minimize insertion trauma.2
- 22 half-banded platinum electrodes arranged in non-uniform spacing from 0.4 to 0.8mm providing focused stimulation to the spiral ganglion cell region over 14.25mm active length.
- Pre-curved design for perimodiolar placement, reduces spread of excitation3 and maximizes hearing performance.4-6
- 19.2mm intracochlear length providing optimal hearing zone coverage.
- 3 silicone ribs to indicate insertion depth.
- Two extracochlear electrodes (one on the receiver/stimulator and one on the extracochlear electrode lead) designed to provide individualized stimulation and mapping.
- White marker to facilitate Advance Off-Stylet® (AOS™) insertion and indicate insertion depth when the tip is close to the lateral wall of the cochlea.
- Basal diameter at 0.8mm.
- Platinum stylet holds the electrode straight for insertion with AOS surgical technique.
Technical Specifications Sheet
Contour Advance Electrode (CI612) Technical Specifications Sheet
Disclaimer
This material is intended for health professionals. If you are a consumer, please seek advice from your health professional about treatments for hearing loss. Outcomes may vary, and your health professional will advise you about the factors which could affect your outcome. Always read the instructions for use. Not all products are available in all countries. Please contact your local Cochlear representative for product information.
For a full list of Cochlear’s trademarks, please visit our Terms of Use page.
References
- FUN1142 Electrode Comparison Chart.
- Roland J T, A model for cochlear implant electrode insertion and force evaluation: Results with a new electrode design and insertion technique, Laryngoscope, vol. 115, pp. 1325-1339, 2005.
- Hughes ML, Stille LJ. Effect of stimulus and recording parameters on spatial spread of excitation and masking patterns obtained with the electrically evoked compound action potential in cochlear implants. Ear Hear. 2010;31:679–92
- Xi X, Ji F, Han D, Hong M, Chen A. Electrode interaction in cochlear implant recipients: comparison of straight and contour electrode arrays. ORL J Otorhinolaryngol Relat Spec. 2009;71(4):228-37. doi: 10.1159/000229303. Epub 2009 Aug 26.
- Basta D, Todt I, Ernst A. Audiological outcome of the pull-back technique in cochlear implantees. Laryngoscope. 2010 Jul; 120(7):1391-6.
- Cohen L, Richardson L, Saunders E, Cowan R: Spatial spread of neural excitation in cochlear implant recipients: comparison of improved ECAP method and psychophysical forward masking Hearing Research 179 (2003) 72-87





